

Dolphins
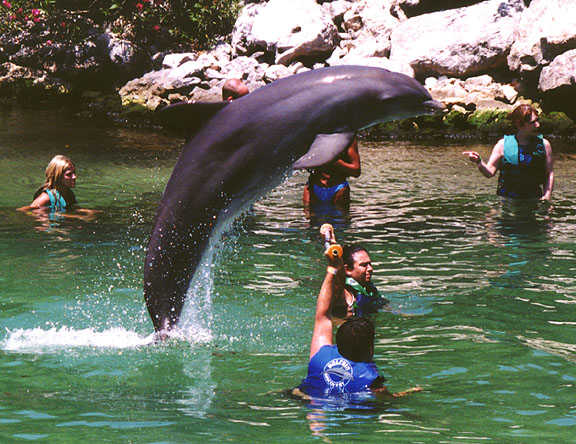

swim with the
Dolphins
(Dolphin Experience at Puerto Aventuras, Mexico)
Dolphin (aquatic mammal), fast-swimming animal related to whales and
porpoises. Sleek and powerful swimmers found in all seas, dolphins are
distinguished from porpoises by well-defined, beaklike snouts and conical teeth.
The porpoise has a blunt snout, chisel-shaped teeth, and a stouter body.
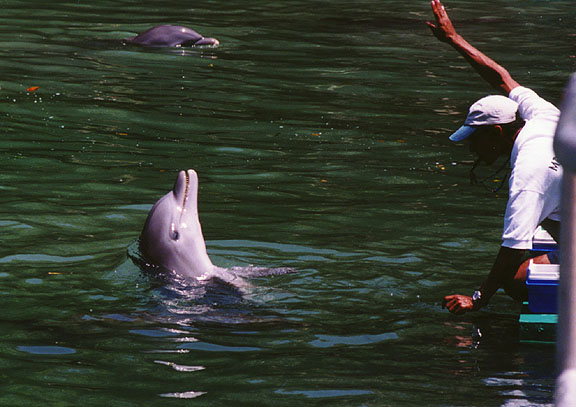

training of the dolphins
There are at least 32 species of dolphins. Typical examples are the bottle-nosed
dolphin, a popular performer in seaquariums, and the common dolphin, which
inspired many Mediterranean folk legends. Both often appear in open waters,
making their characteristic arched bounds, frequently before the bow waves of
ships. Several freshwater species inhabit river estuaries in Asia and South
America. The small, graceful tucuxi dolphin has been sighted more than 2000 km
(more than 1250 mi) up the Amazon River. The tucuxi, the smallest dolphin, is
less than 1.2 m (less than 4 ft) long; the largest, the bottle-nosed dolphin,
reaches a length of 3 m (10 ft). The killer whale is considered a dolphin
despite its much greater length of 9 m (30 ft). The pilot whale is also
considered a type of dolphin.

being pushed by two dolphins

one on each foot
Dolphins once were hunted commercially, especially for the small quantity of
valuable oil extracted from parts of the head and used to lubricate delicate
watch mechanisms. Cheaper oils have now been found from other sources, and
dolphins are no longer hunted for this reason. Many dolphins, however, become
accidentally trapped and drowned in tuna nets; between 1959 and 1972 an
estimated 4.8 million dolphins died in this way. Under pressure from animal
rights activists and United States consumers, both domestic and international
tuna canners have refused to accept shipments from fishing fleets that do not
protect dolphins. Concern has also been expressed about the treatment of
dolphins on display in public aquariums and in "swim with the dolphins"
programs. The Marine Mammal Protection Act of 1972, amended in 1988 and 1992,
was passed to prevent exploitation of dolphins and related aquatic animals. The
National Marine Fisheries Service is the principal regulatory agency.

or can be pulled by holding on to the fins
In one day dolphins eat an amount of food, mostly fish and squid, equal to
nearly one-third of their weight. Dolphins are swift enough to easily
outdistance their prey. They seize their catches with jaws that have from 200 to
250 sharp teeth. Dolphins follow schools of fish in groups of varying size. Some
species, such as the Pacific white-sided dolphin, make up aggregations estimated
at tens of thousands of members. Less gregarious species, such as the
bottle-nosed dolphin, join in groups that often contain only a few members.
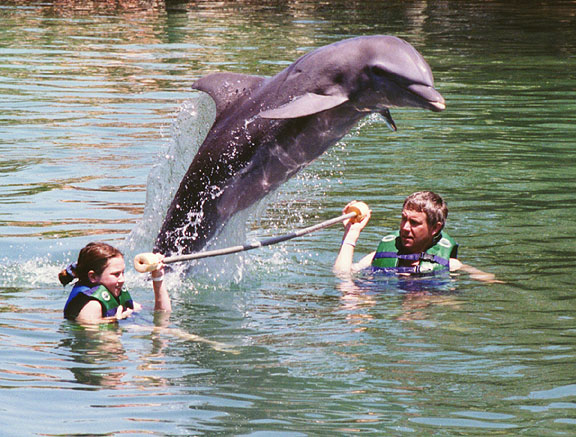
they will jump over a pole
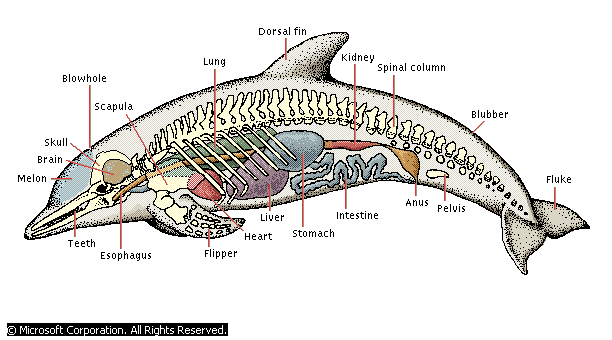
Dolphins, like whales, breathe through a blowhole at the top of the head. As
they travel they break surface about every two minutes to make a short,
explosive exhalation, followed by a longer inhalation before submerging again.
The tail, like that of other aquatic mammals, strokes in an up-and-down motion,
with the double flukes driving the animal forward; the flippers are used for
stabilization. Dolphins are superbly streamlined and can sustain speeds of up to
30 km/h (up to 19 mph), with bursts of more than 40 km/h (more than 25 mph).
Their lungs, which are adapted to resist the physical problems created for many
animals by rapid changes in pressure, enable them to dive to depths of more than
300 m (more than 1000 ft).

show their mouths with teeth
Adults of the bottle-nosed dolphin—the best-studied species—come to sexual
maturity after 5 to 12 years in females and 9 to 13 years in males. They mate in
the spring; after a gestation period of 11 or 12 months, a single calf is born,
tail first. Calves swim and breathe minutes after birth; they nurse for up to 18
months. They are able to keep up with the mother by remaining close and taking
advantage of the aerodynamic effects of the mother’s swimming.
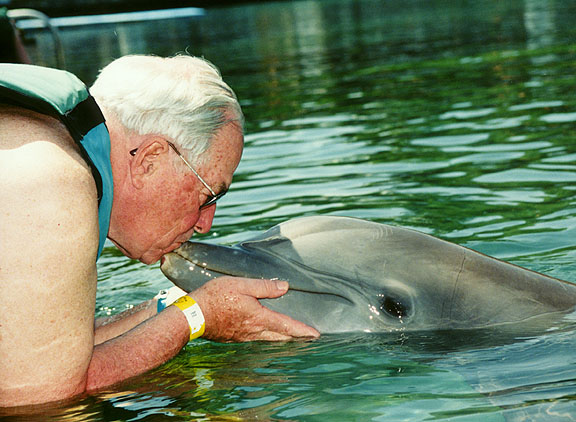

Galen kissing the dolphin
Dolphins almost constantly emit either clicking sounds or whistles. The clicks
are short pulses of about 300 sounds per second, emitted from a mechanism
located just below the blowhole. These clicks are used for the echolocation of
objects and are resonated forward by the so-called oily melon, which is located
above the forehead and acts as an acoustic lens. Echoes received at the area of
the rear of the lower jaw are transmitted by a fat organ in the lower jaw to the
middle ear. This echolocation system, similar to that of a bat, enables the
dolphin to navigate among its companions and larger objects and to detect fish,
squid, and even small shrimp. The whistles are single-toned squeals that come
from deeper in the larynx. They are used to communicate alarm, sexual
excitement, and perhaps other emotional states.
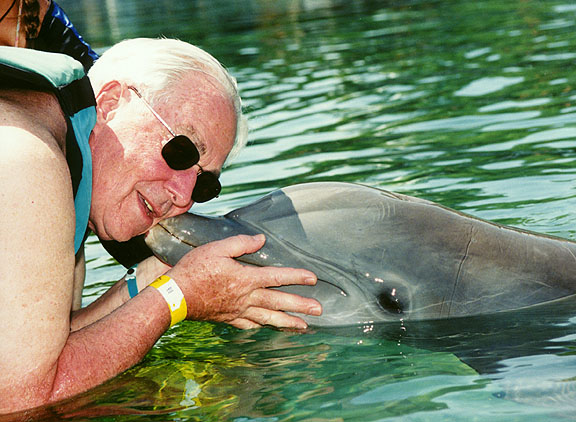

Galen being kissed
Because of the ability of dolphins to learn and perform complex tasks in
captivity, their continuous communications with one another, and their ability,
through training, to approximate the sounds of a few human words, some
investigators have suggested that the animals might be capable of learning a
true language and communicating with humans. Most authorities, however, agree
that although the dolphin’s problem-solving abilities put the animal on an
intelligence level close to that of primates, no evidence exists that dolphin
communications approach the complexity of a true language.
The name dolphin is also applied to food fish of a different genus that
have long, continuous dorsal fins. The fish, found worldwide in tropical marine
waters, can reach a length of 1.5 m (5 ft).

another jump
Scientific classification: Dolphins belong to the suborder Odontoceti of
the order Cetacea. The bottle-nosed dolphin is classified as Tursiops truncatus,
the common dolphin as Delphinus delphis, and the tucuxi dolphin as
Sotalia fluviatilis. The killer whale is classified as Orcinus orca.
Pilot whales make up the genus Globicephala. The white-sided dolphin is
classified as Lagenorhynchus obliquidens.
Text from Microsoft Encarta

an extra push
![]()
Return to Favorite Animals page
![]()