Toledo

Toledo (Spain), city, central Spain, capital of Castile-La Mancha region and of Toledo Province, on the Tajo (Tagus) River, near Madrid. The city is built on a promontory, about 732 m (about 2400 ft) above sea level, bordered on three sides by a gorge in the Tajo, with the land side protected by an inner and outer wall. The most famous industry is the manufacture of swords, both by private companies and by a government factory. Other manufactures include beer, confectionery, church ornaments, textiles, bricks, and fans.

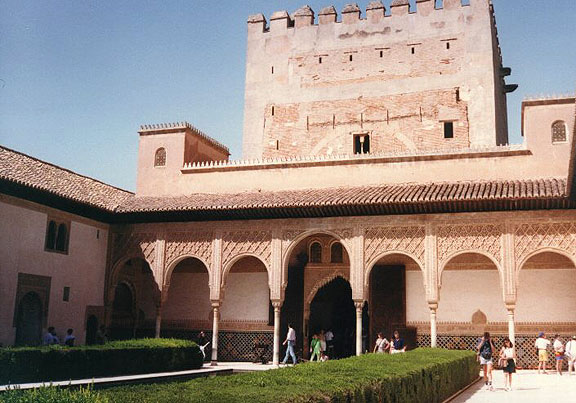
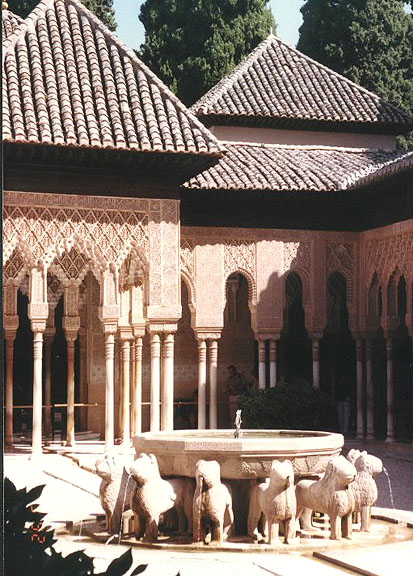
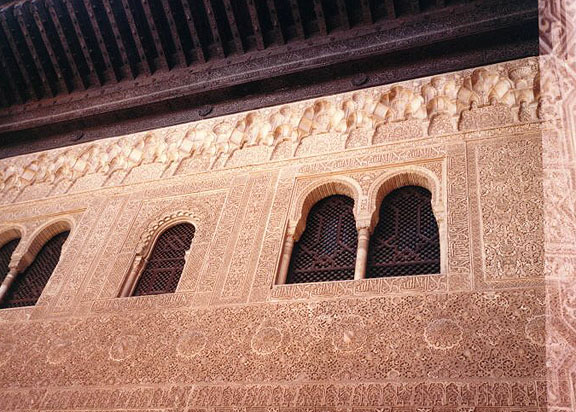
Toledo has many towers, old gates, narrow, winding streets, massive houses, and predominantly Moorish architecture, which give it a medieval atmosphere.

In the center of the city rises the principal edifice, a Gothic cathedral (1227-1493) with 40 chapels. Other noteworthy architectural features are the Gothic Church of San Juan de los Reyes and its adjoining convent, a gift (1476) of Ferdinand V, king of Castile, and his wife Isabella I; El Tránsito, a synagogue (1366) that was converted to a church after the expulsion of the Jews in 1492; and the Church of Santo Tomé, originally a mosque and rebuilt as a Gothic church in the 14th century.

The churches of Toledo contain some of the greatest works of art in Spain, notably those by the painter El Greco.

On the highest ground stands the Alcázar, a vast, square edifice with four towers, now a military academy, around which the houses of Toledo are grouped in a semicircle. The Plaza de Zocodover, built in the 7th century and later rebuilt by Moorish invaders, is a fashionable promenade and was long the site on which victims of the Inquisition were burned and bullfights took place.

Of pre-Roman origin, the city fell to the Romans about 193BC and was named Toletum. From about AD534 to 712, Toledo was the capital of the Visigothic kingdom in Spain and became a great ecclesiastical center. After its conquest (712) by the Arabs, the city became an important Moorish center and in the 11th century the capital of a short-lived Moorish kingdom (1035-85). In 1085, after a memorable siege, the city was captured by the forces of Castile and annexed to the Castilian realms, of which it was made the capital (1087-1560). From July to September 1936, during the Spanish Civil War, rebel forces in the Alcázar were besieged for 70 days by Loyalist, or Republican, forces. Population (1991) 63,561.



windmills

advertising bull
![]()
Granada